Data View
The Data view allows you to view and export data extracted by Robots. It can only be used to show database tables created from types, either using Design Studio or Management Console.
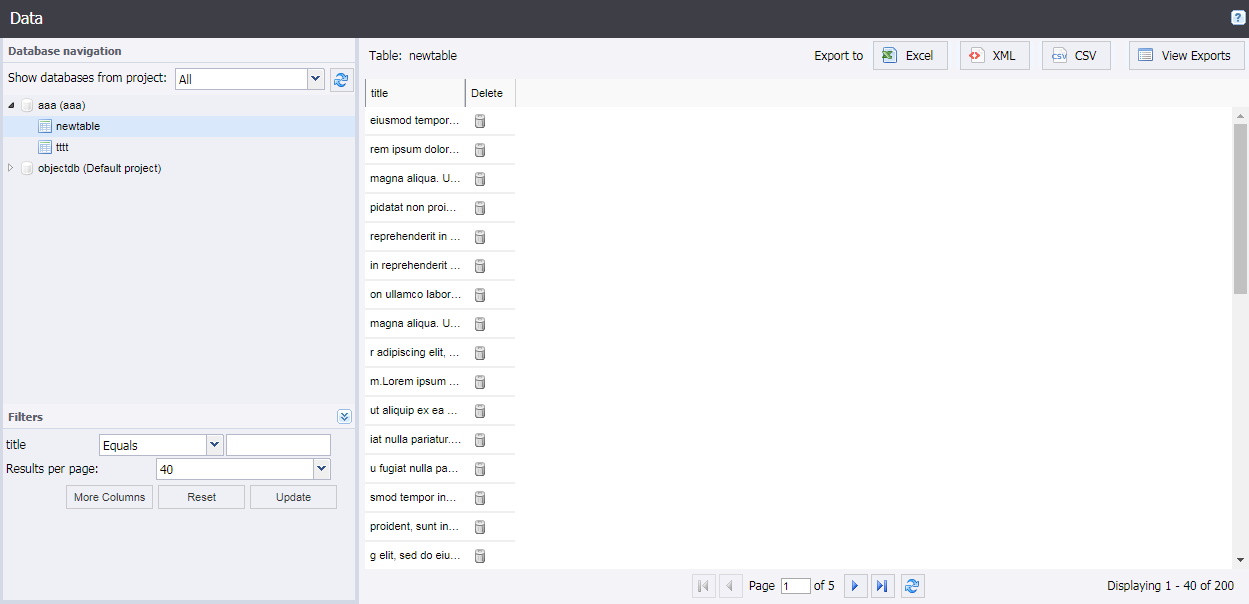
In the upper left corner of the Data view, you can see the Database navigation tree along with a project selector. You can view data from the databases for each project. To view data from a given project, select it, and the database mappings defined in that project will be shown in the database navigation tree. Next to the project selector is a refresh button for use when the databases have changed, in which case it will re-populate the database navigation tree to show the new information.
When you click a database mapping name, the tree opens, and you can see the various schemas in the database. When you click a schema you can see the Kofax RPA tables in that schema. When you click a table, the contents of that table are loaded into the data grid on the right pane. Once the data is loaded, a number of filters become visible in the Filters window. The filters work exactly like the filters on the Logging Tab. Binary and longtext attributes are not filterable.
If you click the Delete column, a window will open allowing you to delete one or more rows for the table. Double clicking a row will bring up a window with the content of that row, allowing you to copy the data.
Above the data grid, you can see an Export bar, containing 4 buttons. The first 3 buttons allow you to export the table data to either Excel, XML, or CSV format. The fourth button allows you to see previous export, and download them again. The exports are automatically deleted the next time the Management Console starts, also the oldest exports are deleted when the number of exports exceeds 100. There is no limit to the number of rows you can export to CSV or XML, but Excel files are limited to 10000 records, to prevent the system from running out of memory.
The list of schemas/catalogs available under each database in the navigation tree, is controlled by the permissions of the user who's credentials are used (in the cluster settings database configuration).
